
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interesting Ocean Facts |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Area: about 140 million square miles (362 million sq km), or nearly 71% of the Earth's surface. Average Depth: 12,200 feet (3,720 m). Deepest point: 36,198 feet (11,033 m) in the Mariana Trench in the western Pacific. Mountains: The ocean ridges form a great mountain range, almost 40,000 miles (64,000 km) long, that weaves its way through all the major oceans. It is the largest single feature on Earth. Highest Mountain: Mauna Kea, Hawaii, rises 33,474 feet (10,203 m) from its base on the ocean floor; only 13,680 feet (4,170 m) are above sea level. 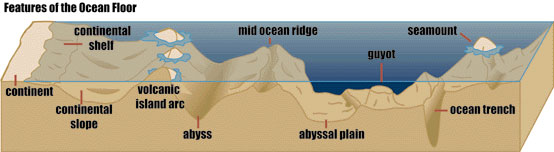 Help Further Humanity with these lovely gifts shown below.. A portion of ALL proceeds received by this artist and these designs are directly donated to humanitarian causes and nonprofit organizations that help move the world forward.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
48 more facts about our oceans...
Coastlines The total length of the world's coastlines is about 315,000 miles, enough to circle the Equator 12 times. As coastal zones become more and more crowded, the quality of coastal water will suffer, the wildlife will be displaced, and the shorelines will erode. 60% of the Pacific and 35% of the Atlantic Coast shoreline are eroding at a rate of a meter every year. More than half the world’s population live within a 100 km or 60
miles distance from the coast. This is more than 2.7 billion people.
Rapid urbanization will lead to more coastal mega-cities containing 10
million or more people. By the end of the millennium 13 out of 15 of the
world’s largest cities will be located on or near the coast. Growing
population in coastal areas leads to more marine pollution and
distribution of coastal habitats. Some 6,5 million tons (6,500,000,000
kilo) of litter finds its way into the sea each year. The sea provides the biggest source of wild or domestic protein in the world. Each year some 70 to 75 million tons of fish are caught in the ocean. Of this amount around 29 million tons is for human consumption. The global fish production exceeds that of cattle, sheep, poultry or eggs. Fish can be produced in two ways: by capture and by aqua culture. The total production has grown 34% over the last decade. The largest numbers of fish are located in the Southern Hemisphere due to the fact that these waters are not largely exploited by man. Fifteen out of seventeen of the world's largest fisheries are so heavily exploited that the reproduction can't keep up. With the result that many fish populations are decreasing rapidly. Species of fish endangered by overfishing are: tuna, salmon, haddock, halibut, and cod. In the 19th century, codfish weighing up to 200 pounds used to be caught. Nowadays, a 40 pound cod is considered a giant. Reason: overfishing. Rising Sea Level The sea level has risen with an average of 4-10 inches (10 to 25 cm) over the past 100 years and scientists expect this rate to increase. Sea levels will continue rising even if the climate has stabilized, because the ocean reacts slowly to changes. 10,000 years ago the ocean level was about 330 ft (110 mtr) lower than it is now. If all the world's ice melted, the oceans would rise 200 ft (66 mtr). Volcanic Activity 90% of all volcanic activity on Earth occurs in the ocean. The largest known concentration of active volcanoes (approximately 1,133) on the sea floor is located in the South Pacific Density The density of ocean water varies. It becomes more dense as it becomes colder, right down to its freezing point of -1.9 degrees C. (This is unlike fresh water, which is most dense at 4 degrees C, well above its freezing point.) Water temperature Under the enormous pressures of the deep ocean, sea water can reach very high temperatures without boiling. A water temperature of 400 degrees C has been measured at one hydrothermal vent. The average temperature of all ocean water is about 3.5° C. Almost all of the deep ocean temperatures are only a little warmer than freezing (39°F). Ice Antarctica has as much ice as the Atlantic Ocean has water. 10% of the earth's surface is covered with ice. The Arctic Ocean is the smallest ocean, holding only one percent of the Earth's seawater. This is still more than 25 times as much water as all rivers and fresh water lakes. The average thickness of the Arctic ice sheet is about 9 to 10 feet, although there are some areas as thick as 65 feet. In the unlikely event that all the polar ice were to melt, the sea level all over the world would rise 500 to 600 feet. As a result, 85 to 90% of the Earth's surface would be covered with water as compared to the current 71%. The U.S. would be split by the Mississippi Sea, which would connect the Great Lakes with the Gulf of Mexico. The Arctic produces 10,000 to 50,000 icebergs annually. The amount produced in the Antarctic regions is inestimable. Icebergs normally have a four-year life-span; they begin entering shipping lanes after about three years. Carbon Dioxyde Absorbtion Oceans absorb between 30% and 50% of the carbon dioxide produced by burning fossil fuel. Carbon dioxide is transported downwards by plankton. Any change in the temperature of the ocean water, influences the ability of plankton to take up carbon dioxide. This has consequences for the ecosystem, because plankton form the base of the food web. Reefs Over 60% of the world's coral reefs are threatened as a result of pollution, sedimentation and bleaching due to rising water temperatures caused by global warming. Global Coral Monitoring Network (GCRMN) states that currently 27% of all coral reef worldwide has disappeared and around 2050 only 30% will be left. Rubbish/Contamination In one year, three times as much rubbish is dumped into the world's oceans as the weight of fish caught. A single quart of motor oil can contaminate up to 2 million gallons of drinking water.
If all the gold suspended in the world's seawater were mined, each person on Earth could have about 9 pounds of gold. Oil Oil is one of the ocean's greatest resources. nearly one-third of the world's oil comes from offshore fields in our oceans. Areas most popular for oil drilling are the Arabian Gulf, the North Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico. Salinity Some scientists estimate that the oceans contain as much as 50 quadrillion tons (50 million billion tons=50,000,000,000,000,000) of dissolved solids. If the salt in the ocean could be removed and spread evenly over the Earth’s land surface it would form a layer more than 500 feet (166 m) thick, about the height of a 40-story office building. The ocean's principal dissolved solids are sodium salts (sodium chloride or common salt), calcium salts (calcium carbonate or lime, and calcium sulfate), potassium salts (potassium sulfate), and magnesium salts (magnesium chloride, magnesium sulfate, and magnesium bromide). Atlantic sea water is heavier than Pacific sea water due to its higher salt content. The freezing point of sea water depends on its salt content. Typical ocean water has about 35 grams of salt per liter and freezes at -19 degrees C.
Desalination Arabian Gulf reverse osmosis plants treat 500,000,000 gallons of sea water to obtain 100,000,000 gallons of fresh water. Daily over 500,000,000 gallons of Seawater must be heated to extremely high temperatures. Mixed with toxic chemicals the Seawater is injected under high pressure through a series of membrane filters. Only 100,000,000 gallons of fresh water is generated. The 5:1 ratio of this highly inefficient process means 400,000,000 gallons of untreated water are returned to the sea each day. The higher temperature of the discharged water causes environmental problems. Worse, the super heated brine discharge has significantly higher levels of total dissolved solids, and toxic chemicals are mixed in with it. This pollution is usually discharged back into the sea. The 10 Largest Territorial Powers (in million sq km's)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||